XDR Agent Installation - Crime
We have developed a method of installing the XDR agent to Crime VMs. This differs from the HMCTS install method which utilised the VM Extension capability on Azure VMs and is delivered via Terraform.
For Crime, we are utilising Ansible as the delivery method and have developed an Ansible Role which will perform the installation.
To trigger the Ansible, we use the pre-existing adhoc pipelines in the main Crime Jenkins instance which can be scope limited by Ansible’s Limit functionality. These are also limited in scope with an adhoc pipeline for each environment and a stack selection parameter. This enables us to follow a rollout plan through environments and safely stage our delivery.
This document details the procedure to do this.
Declaring xdr_tags
ANSIBLE_EXTRA_VARS Parameter
xdr_tags is the only ansible variable that needs declaring for the xdr deployment role to work. There are two ways this can be declared; via the adhoc pipeline ANSIBLE*EXTRA_VARS parameter or via the group/host vars in the automation.ansible repository under _sp-ansible/* directory.
The recommended method is to use the ANSIBLE_EXTRA_VARS parameter. The reasoning for this is that it is much easier to provide via the pipeline parameter compared to updating the automation.ansible group/host vars. Also, moving forward we will be trying to avoid VM deployments in the future so for the time being the role will not be included in the main deploy.yml playbook in automation.ansible. This is the playbook which is run against VMs to install/configure them with things required by Crime Platops.
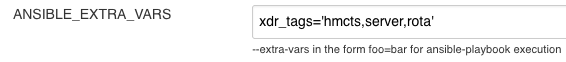
Provide ANSIBLE_EXTRA_VARS in the format above. This is a string with each tag separated by a pipe symbol.
An MS Team channel exists called “HMCTS - Tagging Catch Up” with the MoJ SoC team as members. Please reach out to MoJ SoC if unsure of tags to use.
Other Role variables
Other variables are defaulted within the Role and do not need setting in automation.ansible repo inventory.
As MoJ SoC use their ‘nonprod’ instance of Cortex XSIAM more like a sandbox instance, all VMs whether nonlive or live should use the ‘prod’ XDR installer package. As such, this is now set in the role defaults and doesn’t need defining explicitly in group or host vars.
The only exception to this is ‘sa_key’. This has been set on the ‘all’ group and is already usable by all hosts.
Declaring xdr_tags through Host/Group vars - Not Recommended
This is not the recommended method for declaring xdr_tags however it can be done this way.
Declare in either Ansible group_vars or host_vars:
Example:
xdr_tags: "hmcts,server,idam"
These need setting in the automation.ansible repository. The vars live at /sp-ansible/group_vars & /sp-ansible/host_vars. Information on Ansible variables is available in the official documentation.
Its possible the level to set these variables doesn’t have a pre-existing vars file. e.g. there may not be a host_vars/X file for your host or a group_vars/X file for the group level. The vars file can be created as necessary.
Deploying the XDR agents
Pipelines
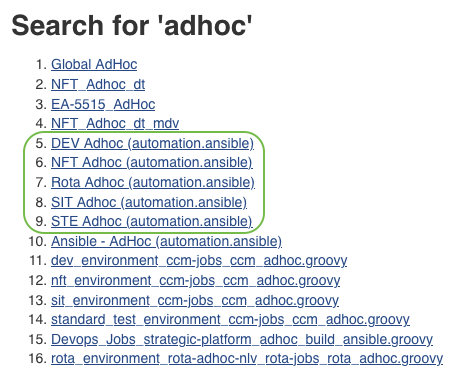
The pipelines in Jenkins for deployment are the pre-existing adhoc pipelines. There is an adhoc pipeline per crime environment. These can be found by searching adhoc in Jenkins:
Using the Pipelines
Pick the pipeline for the applicable environment. These are paramatised:
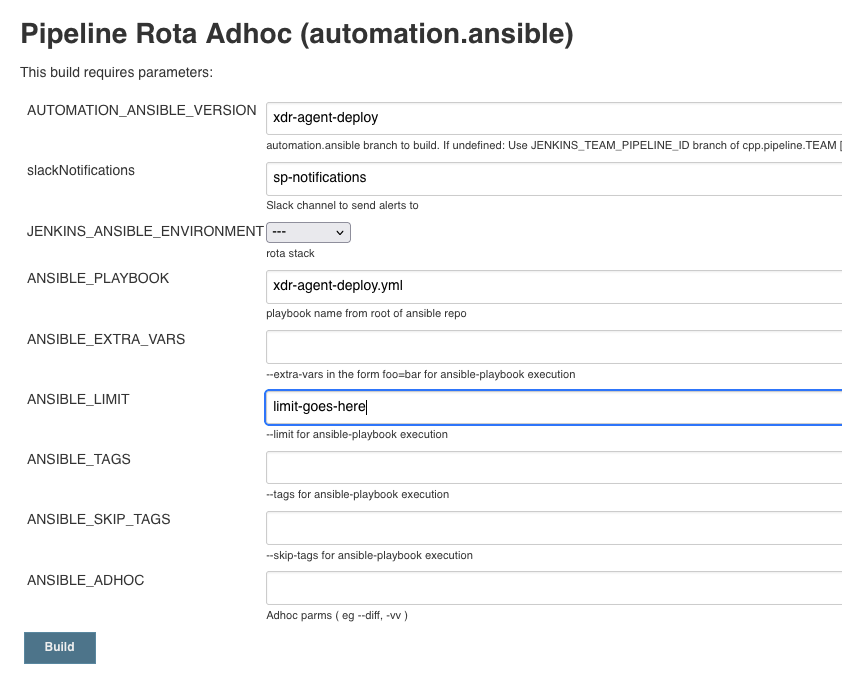
AUTOMATION_ANSIBLE_VERSION
This is the branch of automation.ansible to use. The xdr-agent-deploy playbook is currently only in the xdr-agent-deploy branch with a view of merging to master in the future.
For now set this as xdr-agent-deploy.
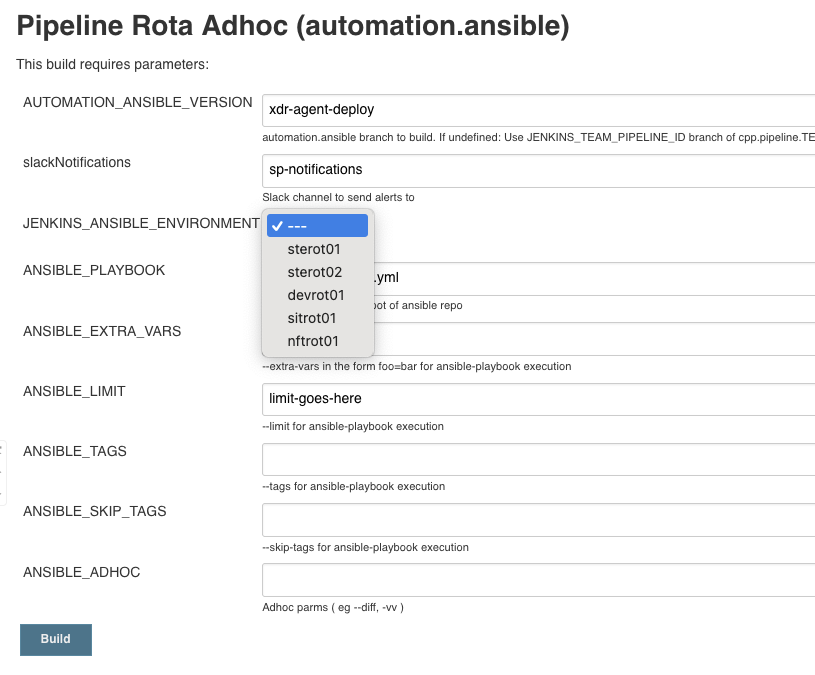
JENKINS_ANSIBLE_ENVIRONMENT
This is named strangely. This sets the stack to target. All stacks for the environment will be available in the dropdown.
This option must be chosen.
ANSIBLE_PLAYBOOK
This is the playbook to run. Set this to xdr-agent-deploy.yml.
ANSIBLE_EXTRA_VARS
See section above on how to set xdr_tags with this parameter.
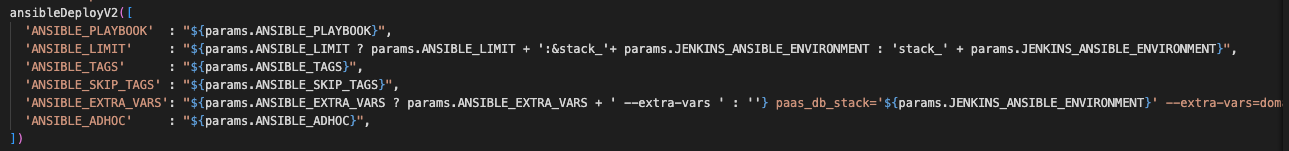
ANSIBLE_LIMIT
This is the ansible limit field. In the backend of Jenkins this is how the limit is formed:

'ANSIBLE_LIMIT' : "${params.ANSIBLE_LIMIT ? params.ANSIBLE_LIMIT + ':&stack_'+ params.JENKINS_ANSIBLE_ENVIRONMENT : 'stack_' + params.JENKINS_ANSIBLE_ENVIRONMENT}"
The ANSIBLE_LIMIT provided in the box is combined with the stack that is chosen for JENKINS_ANSIBLE_ENVIRONMENT to form the true limit string that is fed to the ansible-playbook command.
An example of this where a single host is given as the limit:
DEVROT01AAPSV01.cpp.nonlive:&stack_devrot01:stack_devrot01
Why the stack is repeated twice is unknown however there is probably an underlying reason. The duplication does not alter the end result of the limit.
The end result of the limit is the intersection of VMs given to ANSIBLE_LIMIT parameter and the stack that is chosen. So VMs that are targeted are those that are in both of the groups for example.
This underlying formulation of the true limit restricts the scope of VMs which can be targeted. This makes it much safer to run given the ANSIBLE_LIMIT parameter can be left empty or given the * character which acts as a wildcard for all. Without this the scope it would be possible to target all VMs in the Strategic subscription (Strategic non-live for .non-live Jenkins, Strategic live for .live Jenkins).
All Other Parameters
All other parameters should be left blank.
Azure Inventory Script & Determining ANSIBLE_LIMIT Param
Ansible in automation.ansible repo utilises a inventory script which dynamically queries Azure and fetches existing VMs. It does this on a subscription level and groups the VMs in the following way:
- azure
- location
- resource_group
- security_group
- tag key_value
tag key_value groups by Azure tags. Each Azure tag key & value form its own group in the syntax:
key_value
e.g:
[environment_dev]
Host1
Host2
Host3
As seen in the ANSIBLE*LIMIT section above, the true limit passed to the ansible-playbook command is using a _tag key_value* group. This is the stack tag on VMs in Azure.
Crime use different tags to tag useful information about a VM to the VM in Azure. Other tags include application, tier, stack, project & platform.
Teams rolling out xdr agents should formulate a strategy utilising these tag groupings. For instance, if the rollout strategy requires targeting a tier at a time then investigate the tier tagging across the environment and utilise this in your limiting.
The ANSIBLE_LIMIT does not have to be a single host or group, it can be a pattern also. For instance:
application_rota:&tier_rot
This will combine to form a true limit of:
application_rota:&tier_rot:&stack_devrot01:stack_devrot01
The end result targets VMs which are members of all three groups (so VMs which are tagged with these key value combinations):
- application_rota
- tier_rot
- stack_devrot01
If combining groups to form a pattern for ANSIBLE*LIMIT, in most cases the *:&_ operator should be used. This specifies the limit should only be VMs that intersect all three groups.
Information on Ansible limiting is available in the official documentation.
Jenkins
Crime have multiple Jenkins instances, some are application specific (such as build-idam) and these live as deployments in AKS. The main PlatOps Jenkins is deployed as a VM (active & standby pairing) & separate instances exist for non-live & live:
- build[.]mdv[.]cpp[.]nonlive
- build[.]mdv[.]cpp[.]live
The Role
All installation code is contained within the Role. The playbook xdr-agent-deploy executes only calls the Role. The Role code is separated into its own repository
The Role makes use of the same Shared Access Signature token used in the HMCTS XDR install process for HMCTS. azcopy is installed and used to retrieve the installation package & config from cftptlintsvc storage account under the xdr-collectors blob.
The SAS token itself is stored in Vault and Ansible’s Vault lookup plugin is used to fetch this value.
The Role has the ability to update tag information in-place. Simply update xdr_tags variable and re-run the xdr-ansible-deploy pipeline.
Verify Installation
Verify installation in the Cortex XSIAM Portal. Certain PlatOps members have access (Rees, Chirag, Jordan H). This can also be confirmed by MOJ SoC Engineers in the MS Teams chat.
Verification can also be made on the VM itself.
rpm -qa | grep -i cortex-agent
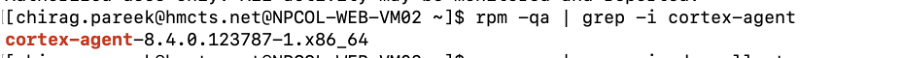
To check the agent is running on the VM:
systemctl status traps_pmd.service
Uninstall
If required, uninstall the XDR agent by doing the following:
Verify agent is installed
rpm -qa | grep -i cortex-agent
If installed, run the rpm erase command
rpm -e cortex-agent
If this fails to work, specify the full version (this will have been output from the first command).
For example
rpm —e cortex-agent-8.5.0.125392-1.x86_64
This will automatically remove the VM from the XSIAM Cortex portal
Developing the Role
We have created a test environment repo which mimics the python & ansible setup used in Crime’s main PlatOps Jenkins instance.
The README details how to setup a local machine environment for development that is compatible with the Jenkins environment. It uses Vagrant & the Virtualbox driver to build a local VM and automate Ansible against it.
Troubleshooting
Put troubleshooting info here as needed